Marketing Mix: 4Ps, 7Ps, 4Cs & Digital Strategies
Introduction to Marketing Mix
Concept and Meaning
The Marketing Mix is the “toolkit” of a marketer. It is the set of tactical, controllable tools that a company mixes together to produce the desired response from its target market.
Think of marketing like cooking a dish. You have ingredients like salt, spices, vegetables, and heat.
If you put too much salt (Price is too high), people won’t eat it.
If you don’t serve it on a table (Place is wrong), people can’t eat it.
If you don’t tell anyone it’s ready (Promotion is missing), no one will come.
Definition:
“The Marketing Mix is the set of controllable variables that the firm can use to influence the buyer’s response.” — Philip Kotler
Evolution: From 4Ps to 7Ps
The 4Ps: Proposed by E. Jerome McCarthy in 1960. These are primarily for Physical Products (Soap, Cars, Phones).
The 7Ps: Expanded by Booms and Bitner in 1981. They added 3 extra Ps for Services (Hotels, Airlines, Banks) because services are different from physical goods.

The Traditional 4Ps (Product Marketing Mix)
These four pillars are the foundation of any business strategy.
1. Product (The Solution)
The product is not just the physical item; it is the total bundle of benefits offered to the customer to satisfy a need.
Levels of Product:
Core Benefit: What the customer is really buying (e.g., A car buyer is buying “Transportation”).
Actual Product: The physical device (Engine, Seats, Brand Name).
Augmented Product: Extra services (Warranty, Free Servicing, Financing).
Product Mix Decisions:
Product Line: A group of related products (e.g., Dove Soap, Dove Shampoo).
Product Width: Number of different product lines.
Product Depth: Varieties of each product (e.g., Lux in Pink, White, Blue).
Packaging: It acts as the “Silent Salesman” on the shelf.
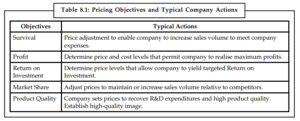
2. Price (The Value)
Price is the exchange value of the product. It is the only P that brings in money; the others cost money. Setting the right price is critical because it directly determines profit.
Factors Affecting Price:
Internal: Cost of production, marketing goals.
External: Competitor prices, demand, government taxes (GST).
Key Pricing Strategies:
Skimming: High initial price for luxury/innovative goods (e.g., iPhone launch).
Penetration: Low initial price to capture market share (e.g., Jio launch).
Psychological Pricing: Pricing at ₹99 instead of ₹100 to make it look cheaper.
Dynamic Pricing: Changing prices based on demand (e.g., Uber surge, Airline tickets).
3. Place (Distribution)
Place does not just mean the shop location; it means Distribution Channels. It is the process of moving the product from the factory to the customer’s hands.
Distribution Channels:
Zero Level (Direct): Manufacturer ——- Customer (e.g., Eureka Forbes, Dell Website).
One Level: Manufacturer ——Retailer ——-Customer (e.g., Cars).
Two Level: Manufacturer ——Wholesaler ——- Retailer ——Customer (e.g., FMCG goods like Soap, Biscuits).
Distribution Strategies:
Intensive: Available everywhere (e.g., Coke, Chips).
Selective: Available in select shops (e.g., TVs, Laptops).
Exclusive: Available in only one shop per city (e.g., Rolls Royce, Rolex).
4. Promotion (Communication)
Promotion is how you tell the world about your product. It persuades customers to buy.
The Promotion Mix:
Advertising: Paid, non-personal communication (TV, Billboards, YouTube Ads). Best for mass reach.
Personal Selling: Face-to-face interaction (Salesmen). Best for expensive/complex products.
Sales Promotion: Short-term incentives to boost sales quickly (Coupons, “Buy 1 Get 1 Free”, Discounts).
Public Relations (PR): Building a good image (Press releases, Sponsorships, CSR activities).
Direct Marketing: Communicating directly with customers (Emails, SMS, Telemarketing).
The Extended 7Ps (Service Marketing Mix)
Services are Intangible (cannot be touched), Inseparable (produced and consumed at the same time), and Variable (quality changes). Therefore, 4Ps are insufficient. We need 3 more:
5. People
Services are performed by people. The quality of the service depends entirely on the employee delivering it.
Significance: A rude waiter ruins the dinner, even if the food (Product) was tasty. A knowledgeable banker builds trust.
Strategy: Training, uniforms, soft skills, and attitude management.
6. Process
The procedure, mechanism, and flow of activities by which the service is delivered.
Significance: If a pizza delivery takes 2 hours instead of 30 minutes, the process has failed. If a bank account opening takes 10 forms, the process is bad.
Strategy: Standardization (McDonald’s assembly line) vs. Customization (Hair salon styling). Efficient processes reduce waiting time.
7. Physical Evidence
Since customers cannot “see” the service before buying, they look for tangible clues to judge quality.
Significance: You judge a hospital by its cleanliness. You judge a lawyer by their office decor. You judge an airline by the staff’s uniform and the plane’s seats.
Examples: Ambience, furniture, brochures, tickets, websites, signage.
The Modern View: The 4Cs
In modern marketing, the focus has shifted from the Seller’s view (4Ps) to the Buyer’s view (4Cs).
| The 4Ps (Seller’s View) | The 4Cs (Customer’s View) | Explanation |
| Product | Customer Solution | Don’t just sell a product; solve a customer’s problem. |
| Price | Customer Cost | It’s not just the price tag; it’s the total cost of ownership (time, effort, maintenance). |
| Place | Convenience | Don’t just focus on shops; make it convenient to buy (Apps, Home Delivery). |
| Promotion | Communication | Don’t just “promote” (one-way); “communicate” and engage (two-way dialogue). |
Marketing Mix in the Digital Era
The internet has revolutionized the Marketing Mix. It is now dynamic and interactive.
Product —–Co-Creation: Customers now help design products (e.g., Lays asking users to suggest flavors). Products like Software (SaaS) are updated instantly.
Price —–Real-Time Pricing: Prices are no longer fixed labels. They change based on user behavior and demand (e.g., Amazon prices fluctuate daily).
Place —-Omnichannel: The “store” is everywhere—in your pocket (Mobile Apps), on your laptop, and on social media (Instagram Shops).
Promotion——Engagement: Marketing is no longer shouting at customers via TV. It is about Content Marketing, Influencers, and Viral Trends where customers talk back.

Why is the Marketing Mix Important?
Creates Synergy: It ensures all elements work together. (e.g., You cannot sell a high-quality luxury watch (Product) in a cheap plastic bag (Packaging) at a roadside stall (Place)).
Differentiation: It helps a company stand out. (e.g., Domino’s differentiated itself not on Product taste, but on Process speed – “30 Mins or Free”).
Resource Allocation: It helps managers decide where to spend money—should we lower the Price or increase Promotion?
Adaptability: It allows firms to respond to changing environments. (e.g., During Covid, restaurants changed their Place strategy to “Home Delivery” to survive).